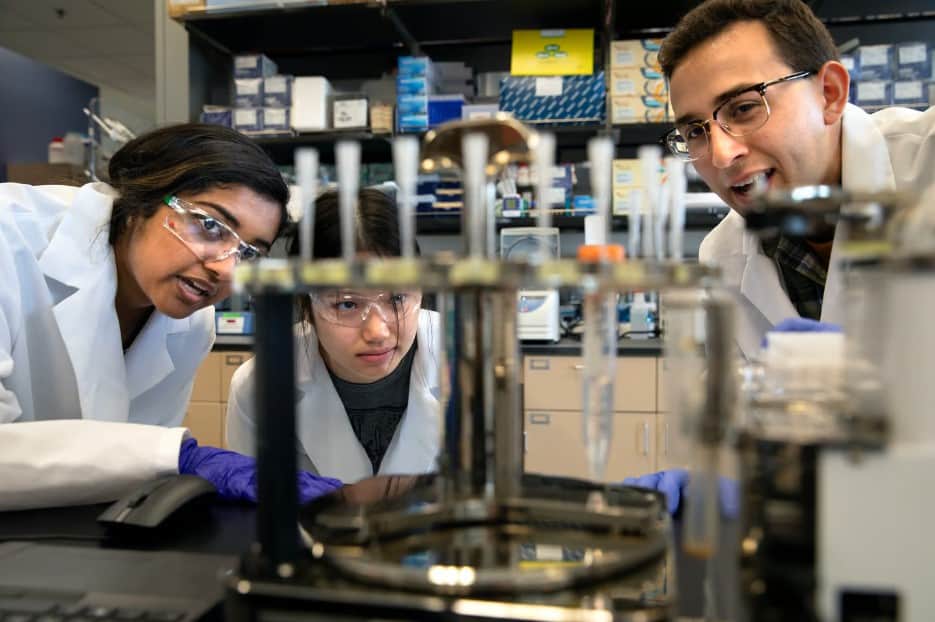
Scientific work often requires analyzing vast amounts of data, which can be tedious for humans but easily accomplished by artificial intelligence.
A recently developed platform called BacterAI can perform up to 10,000 experiments daily, enabling it to learn and help us gain a better understanding of bacteria.
This could also transform the speed of discoveries in medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
The human body contains trillions of tiny organisms, present in nearly every part of it. Some of these organisms are necessary for important bodily functions, while others can cause illness.
Ongoing research is revealing strong connections between our overall health and these microorganisms, but handling and analyzing the data involved is still a challenging task.
“We know almost nothing about most of the bacteria that influence our health, Understanding how bacteria grow is the first step toward reengineering our microbiome,” said Paul Jensen, U-M assistant professor of biomedical engineering.
AI is great at handling large data sets and finding patterns. It’s very useful for scientists studying bacterial data. Usually, they use machine-learning models with existing data sets. But this doesn’t work well when there isn’t much data available for certain bacteria. Sadly, about 90% of bacteria have not been studied much or at all.
Scientists at the University of Michigan have developed BacterAI, a platform that explores bacteria without prior knowledge. It creates its dataset by designing a sequence of experiments for laboratory robots to perform.
The results of each experiment guide the next one. With time, BacterAI synthesizes its findings into logical rules that human scientists can understand and further investigate through additional tests.
BacterAI was used to understand the metabolic processes of two common oral bacteria: Streptococcus gordonii and Streptococcus sanguinis.
It aimed to identify the specific amino acid combinations these bacteria consume from a pool of 20 essential amino acids. This involved exploring over a million potential combinations.
BacterAI can analyze hundreds of amino acid combinations each day and choose the most promising ones for further investigation.
It can conduct up to 10,000 experiments per day. In just nine days, BacterAI achieved a 90% accuracy rate in making accurate predictions.
Unlike standard methods that use labeled data sets for machine learning models, BacterAI creates its data set through a series of experiments.
By studying the results of previous trials, it predicts which experiments will provide the most useful information. As a result, BacterAI identified most of the rules for feeding bacteria with less than 4,000 experiments.

About 90% of bacteria have been the subject of research., and it’s challenging to gather even basic scientific knowledge about them using traditional methods, which are time and resource-consuming.
However, automated experimentation can greatly speed up these discoveries. The team successfully conducted up to 10,000 experiments in a single day.
This approach is not limited to microbiology. By using AI to solve their questions as puzzles through trial and error, researchers from many fields might advance more quickly and discover new opportunities.
“When a child learns to walk, they don’t just watch adults walk and then say ‘Ok, I got it,’ stand up and start walking. They fumble around and do some trial and error first, We wanted our AI agent to take steps and fall down, to come up with its own ideas and make mistakes. Every day, it gets a little better, a little smarter.” said Jensen.